how to draw 3d graph in maple
Matplotlib was introduced keeping in mind, simply two-dimensional plotting. Just at the time when the release of 1.0 occurred, the 3d utilities were developed upon the 2d and thus, we accept 3d implementation of data available today! The 3d plots are enabled by importing the mplot3d toolkit. In this commodity, nosotros will deal with the 3d plots using matplotlib.
Case:
Python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot every bit plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d' )
Output:
With the above syntax three -dimensional axes are enabled and data can be plotted in three dimensions. iii dimension graph gives a dynamic approach and makes information more interactive. Similar two-D graphs, we can utilize dissimilar ways to represent 3-D graph. We can make a scatter plot, contour plot, surface plot, etc. Let's have a expect at different 3-D plots.
Plotting iii-D Lines and Points
Graph with lines and point are the simplest 3 dimensional graph. ax.plot3d and ax.besprinkle are the function to plot line and point graph respectively.
Case ane: 3 dimensional line graph
Python3
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy every bit np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(project = '3d' )
z = np.linspace( 0 , ane , 100 )
x = z * np.sin( 25 * z)
y = z * np.cos( 25 * z)
ax.plot3D(10, y, z, 'green' )
ax.set_title( '3D line plot geeks for geeks' )
plt.bear witness()
Output:
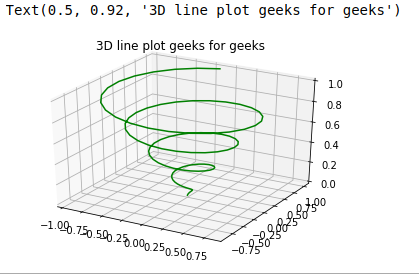
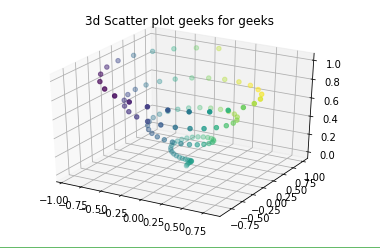
Case 2: iii dimensional scattered graph
Python3
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy every bit np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d' )
z = np.linspace( 0 , ane , 100 )
x = z * np.sin( 25 * z)
y = z * np.cos( 25 * z)
c = x + y
ax.besprinkle(x, y, z, c = c)
ax.set_title( '3d Scatter plot geeks for geeks' )
plt.show()
Output:
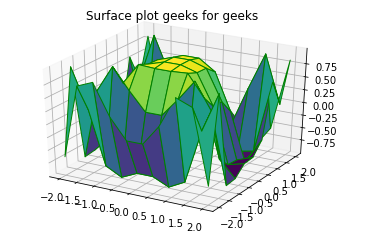
Plotting Surface graphs and Wireframes
Surface graph and Wireframes graph work on gridded data. They take grid value and plot it on 3-dimensional surface.
Example one: Surface graph
Python3
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.outer(np.linspace( - 2 , 2 , ten ), np.ones( 10 ))
y = x.re-create().T
z = np.cos(10 * * 2 + y * * 3 )
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d' )
ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, cmap = 'viridis' , edgecolor = 'light-green' )
ax.set_title( 'Surface plot geeks for geeks' )
plt.show()
Output:
Example 2: Wireframes
Python3
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(x, y):
return np.sin(np.sqrt(x * * 2 + y * * ii ))
x = np.linspace( - 1 , 5 , 10 )
y = np.linspace( - 1 , v , 10 )
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z = f(10, Y)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d' )
ax.plot_wireframe(Ten, Y, Z, color = 'green' )
ax.set_title( 'wireframe geeks for geeks' );
Output:
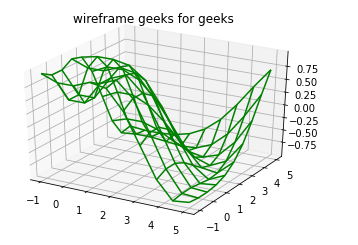
Plotting Contour Graphs
Profile graph takes all the input data in two-dimensional regular grids, and the Z data is evaluated at every point.Nosotros use ax.contour3D role to plot a contour graph.
Example:
Python3
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(10, y):
return np.sin(np.sqrt(x * * 2 + y * * 3 ))
x = np.linspace( - 1 , v , x )
y = np.linspace( - i , v , 10 )
10, Y = np.meshgrid(ten, y)
Z = f(Ten, Y)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d' )
ax.contour3D(X, Y, Z)
Output:
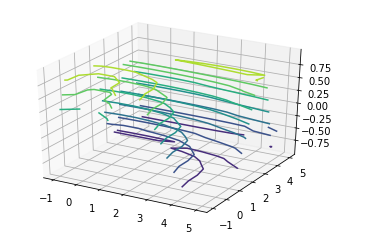
Plotting Surface Triangulations
The higher up graph is sometimes overly restricted and inconvenient. So by this method, we employ a prepare of random draws. The function ax.plot_trisurf is used to draw this graph. It is not that clear but more than flexible.
Example:
Python3
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy every bit np
import matplotlib.pyplot every bit plt
theta = 2 * np.pi * np.random.random( 100 )
r = 6 * np.random.random( 100 )
x = np.ravel(r * np.sin(theta))
y = np.ravel(r * np.cos(theta))
z = f(10, y)
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d' )
ax.scatter(x, y, z, c = z, cmap = 'viridis' , linewidth = 0.25 );
ax = plt.axes(project = '3d' )
ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, cmap = 'viridis' , edgecolor = 'greenish' );
Output:
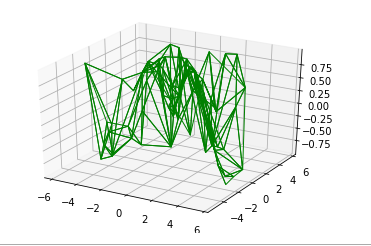
Plotting Möbius strip
Möbius strip also called the twisted cylinder, is a one-sided surface without boundaries. To create the Möbius strip think almost its parameterization, it's a ii-dimensional strip, and we need two intrinsic dimensions. Its bending range from 0 to 2 pie around the loop and width ranges from -one to 1.
Example:
Python3
from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.tri import Triangulation
theta = np.linspace( 0 , two * np.pi, 10 )
west = np.linspace( - ane , five , 8 )
w, theta = np.meshgrid(w, theta)
phi = 0.5 * theta
r = i + westward * np.cos(phi)
ten = np.ravel(r * np.cos(theta))
y = np.ravel(r * np.sin(theta))
z = np.ravel(w * np.sin(phi))
tri = Triangulation(np.ravel(west), np.ravel(theta))
ax = plt.axes(projection = '3d' )
ax.plot_trisurf(x, y, z, triangles = tri.triangles,
cmap = 'viridis' , linewidths = 0.two );
Output:
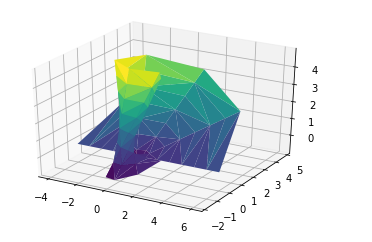
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/three-dimensional-plotting-in-python-using-matplotlib/
0 Response to "how to draw 3d graph in maple"
Enregistrer un commentaire